2024 Organic and Inorganic Compounds SHS Int. Science lesson1 ; WASSCE Standard
WASSCE STANDARD
The lesson specifically follows the WASSCE syllabus, Don’t worry some few things might be missing but your science Teacher will fill the Gap in School. Use this as a Guide.
Organic and inorganic compounds
WASSCE SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
Hydrocarbons (first four members in each group),
alkanols (methanol, ethanol, propanol),
alkanoic acids (first two members),
alkanoates (first two members), fats and oils.
Functional groups, properties and uses of organic compounds.
Classification of chemicals as organic and inorganic
Differences between organic and inorganic compounds.
Importance of organic chemistry in industrialization.
Neutralization And Esterterification.
Differences between neutralization and esterification.
Equations representing neutralization and esterification reactions.
Petrochemical
Sources, application and effects of petrochemicals on the environment.
The refinery of crude oil. Uses of petrochemical such as plastics, pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
Sample past questions
LESSON ONE , TERMS
Definition of keywords and all important Terms
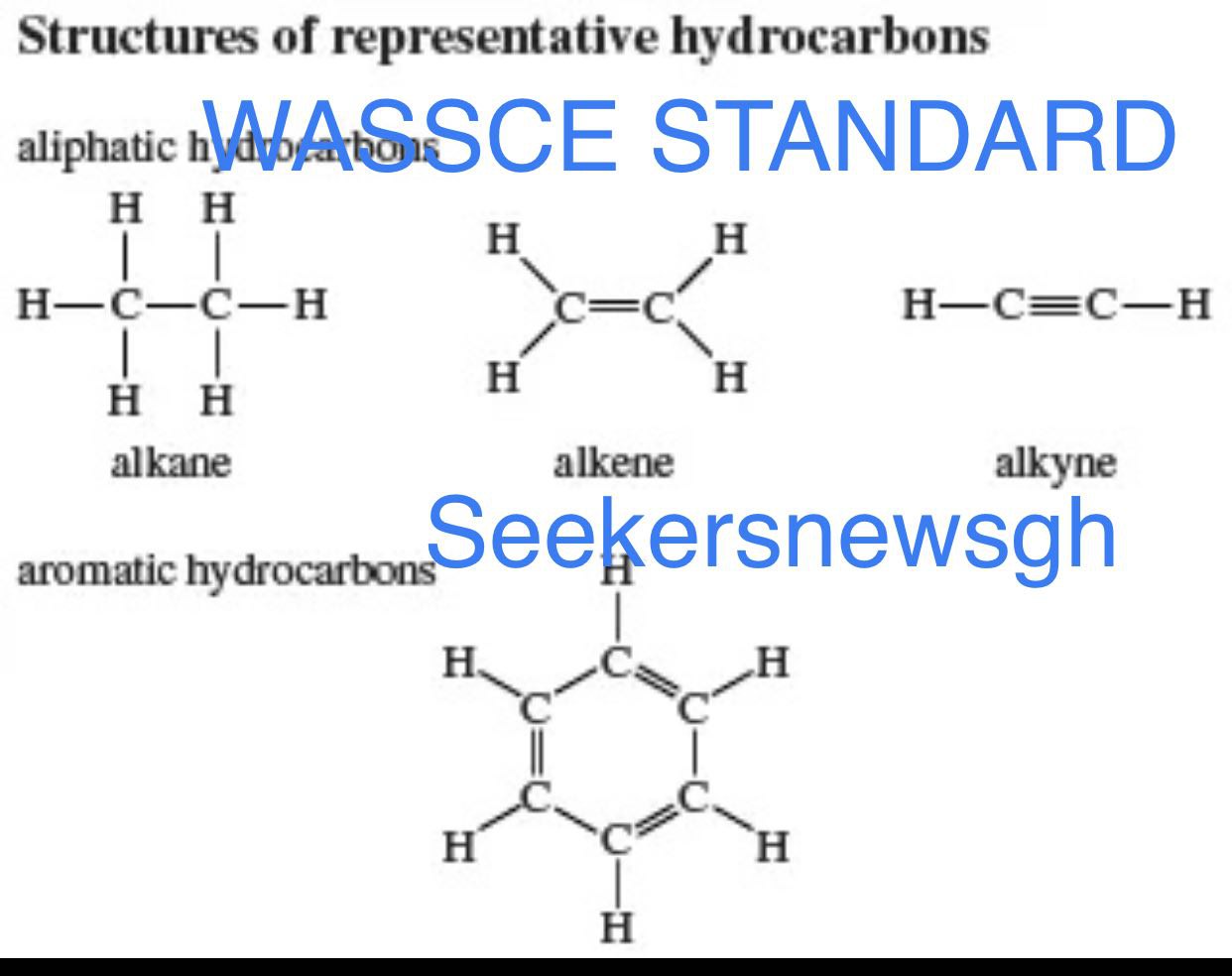
Hydrocarbon; is a compound containing carbon and hydrogen only.
Saturated hydrocarbons; Are organic compounds containing carbon – carbon single bonds only.
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons; Are organic compounds which contain carbon – carbon double or triple bonds.
Functional Group; is an atom or group of atoms or a bond in an organic compound that gives the molecule its characteristic chemical properties.
Cracking; is the breakdown of complex or large molecules of hydrocarbons by action of heat or a catalyst to produce small molecules.
Polymerization; is the combination of small organic molecules (monomers) to form large molecules (polymers)
Saponification; is a reaction between fats or oil and hot concentrated alkali to form soap and glycerol.
Ester ; an Ester is an organic compound produced by the reaction between an organic acid or alkanoic acid and an alcohol or alkanol.
Isomerism; is the occurrence of compounds of the same molecular formular but different structural formular.
Detergent; they are cleaning agents
Or they are substances that have cleaning power and can remove dirt from objects or substances].
Plastics; are polymers of hydrocarbons which can be molded into shapes.
Fats ; are solid esters or lipids obtained from the reaction between glycerol and long chain fatty acids.
Organic compounds ;Organic compounds can be defined as compounds which contain hydrocarbon.
Sources of Organic compounds
- Petroleum (Crude Oil)
2. Natural Gas
3. Coal From plants and Animals
Examples of natural organic compounds
1. Carbohydrates
2. Protein
3. Vitamins
4. Enzymes
5. Hormones
6. Herbs
7. Fats and oils
Examples of artificial organic compounds
1. Plastic
2. Insecticides
3. Pesticides
4. Soap
5. Dyes
6. Drugs etc.
Types of organic compounds
i. Hydrocarbons
ii. Alkanol
iii. Alkanoic acids
iv. Alkanoates
v. Fats and oils.
Hydrocarbons (first four members in each group),
Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons are organic compounds, composed entirely of carbon and hydrogen.
Alkanes – They have single Bonds
Alkenes – they have double bond
Alkynes They have triple Bonds
Aromatic Hydrocarbons – Ring compounds
More in lesson two. You teacher will explain more ……
Inorganic compounds;
Inorganic compounds are compounds which do not contain hydrocarbons.
Examples of inorganic compounds
1. Chalk 2. Salt 3. Washing soda 4. Carbon monoxide, CO 5. Carbon dioxide, CO2 6. Trioxocarbonate (IV), CO3 2-
Differences between organic and inorganic compounds
| Organic Compounds | Inorganic Compounds |
| They mostly have covalent Bonds | They mostly have ionic Bonds |
| Their reactions are very slow | Their reactions are very fast |
| They have low melting points | They have high melting points |
| They have low boiling points | They have high boiling points |
| They are volatile | They are less volatile |
| They are insoluble in water/ soluble in organic solvent | They are soluble in organic solvent/ water |
Your teacher will explain into details during face-to-face lessons
Also wait for Lesson two.
WASSCE Sample Questions Theory
Define Each of the following terms
- Polymerization
- Saponification
- Cracking
- Esterification
- Detergent
- Hydrocarbon
- Fats
- Functional Group
- Plastic
Objective questions will be in the Next lesson
MORE LESSONS
YOU CAN JOIN SHS LEARNERS ON TELEGRAM OR WHATSAPP
List of All Qualified Schools NSMQ 2022
Here are the schools added to NSMQ National Championship 2022 for scoring High Marks
seekersnewsgh.com




