GCSE Grading System 2024
GCSE Grading System
The General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) grading system is used in the United Kingdom to assess the academic achievement of students typically at the age of 16. The system has evolved over the years, it uses letter grades and numbers.
The grading system is as follows:
Grades: The grades are letters, ranging from A* (pronounced “A-star,” the highest grade) to G (the lowest passing grade). However, a grade of G is considered a “standard pass,” and students who achieve a G grade have officially passed the subject.
A*, A, B, and C: These grades are considered “good passes,” with A* being the highest and C being the lowest of the “good passes.”
D and E: These are considered “narrow passes,” with D being slightly higher than E. While they are passing grades, they are not as highly regarded as the A*-C grades.
U (Unclassified): This grade is given when a student’s performance does not meet the minimum standard for a G grade. A U grade means the student has failed that subject.
9-1 Grading Scale: In 2017, England introduced a numerical grading scale for certain subjects, replacing the traditional A*-G system. The scale ranges from 9 (the highest) to 1 (the lowest passing grade). The higher the number, the better the grade.
Mixed Grading System: In some cases, you may find both letter grades and numerical grades on a student’s GCSE certificates. Some subjects have transitioned to the 9-1 scale, while others may still use the A*-G system.
It’s important to note that Scotland has a separate education system, and their qualifications, such as the Scottish National 5 and Higher exams, use different grading systems.
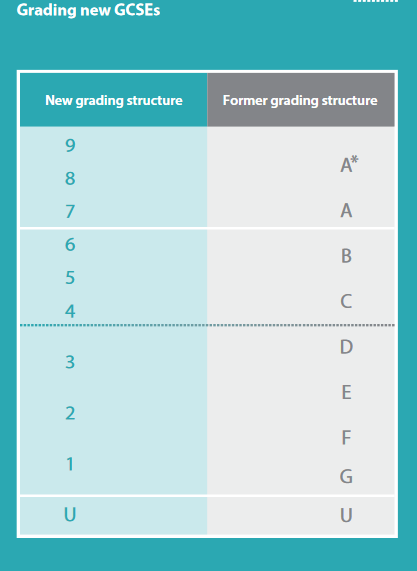
| New Grading System | Old Grading System |
| 9 8 A * 7 A | |
| 6 B 5 C 4 | |
| 3 D 2 E 1 F G | |
| U | U |